Countries set to adopt ‘vital’ pandemic preparedness accord
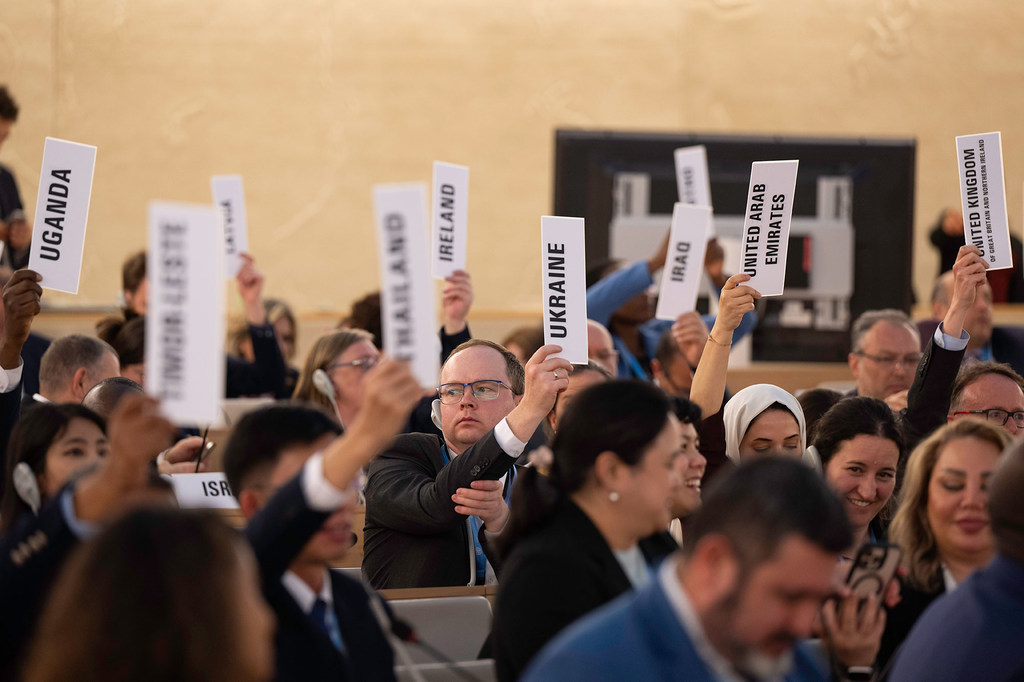
Could the world be better prepared for the next pandemic? As nations continue to deal with COVID-19’s lasting effects, that question is at the heart of an international agreement set to be negotiated in Geneva.
The stakes are high for this year’s World Health Assembly, the UN’s premier health forum, where officials will tackle a sweeping agenda – from pandemic readiness and climate-related health risks to mental health, maternal care, and environmental justice. But with geopolitical tensions running high, international collaboration on these and other vital issues will be tested.
Here are some of the key areas set to dominate discussion:
1. ‘Cautious optimism’: Signing off on a pandemic accord
The COVID-19 pandemic showed that there are stark inequities in access to diagnostics, treatments, and vaccines, both within and between countries. Healthcare services were overwhelmed, economies were severely disrupted and nearly seven million lives were lost.
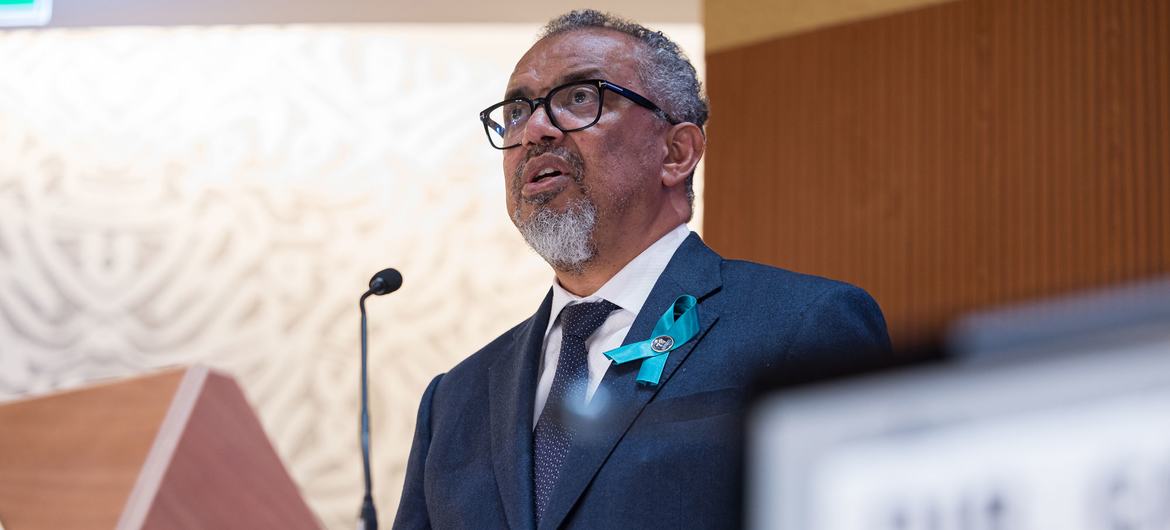
This was the motivation for countries to come together to work on an accord to ensure that the world handles the next pandemic in a fairer and more efficient way. When the delegates arrive in Geneva on Monday 19 May, they will thrash out the text of the agreement, which Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the head of the World Health Organization (WHO), described as “vital for future generations.”
If the agreement is adopted, it will be a major breakthrough in the way the world handles pandemics and health crises. Negotiations, though, remain politically delicate: several nations, including the United States, have raised concerns about national sovereignty and intellectual property rights. Still, in recent weeks, Dr. Tedros has expressed “cautious optimism” that consensus can be reached.
2. Climate Change: An existential threat
The climate crisis isn't just about rising temperatures – it’s putting lives at risk. Extreme weather and disease outbreaks are on the rise, threatening the health of millions. An action plan created by WHO calls for climate and health policies to work together, strengthens resilience, and ensures funding to safeguard vulnerable communities.
A draft version of the plan was released following a resolution adopted at the 2024 conference and, this year, delegates are expected to finalise the draft, which includes strategies to adapt to and mitigate climate-related health risks.
3. Health for all: Getting universal health care back on track
Ensuring that all people have affordable access to the full range of quality health services they need is one of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which all UN Member States signed up to in 2015. However, the health target is way off track: in fact, improvements to health services have stagnated over the last ten years.
Nevertheless, universal health care (UHC) will be a top priority at the Assembly, where delegates will discuss strategies to strengthen primary healthcare systems, secure sustainable financing and provide care for vulnerable populations.
4. Healthy Beginnings: Maternal and newborn health
Close to 300,000 women lose their life during pregnancy or childbirth each year, while over two million babies die in their first month of life. In April, WHO launched a year-long campaign to end preventable maternal and newborn deaths.
Titled “Healthy beginnings, hopeful futures”, it will urge governments and the health community to ramp up efforts to end preventable maternal and newborn deaths, and to prioritize women’s longer-term health and well-being.
Expect new targets and renewed commitments to end preventable deaths to be announced at the Assembly.
5. Closing the gaps: Noncommunicable diseases
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, kill tens of millions of people each year. Around three-quarters of those deaths are in low and middle-income countries.
Many lives could be saved if more countries had strong national responses, providing detection, screening and treatment, as well as palliative care.
In preparation for a WHO meeting on NCDs and mental health in September, delegates will review the way the UN health agency collaborates with governments, civil society, and the private sector to prevent and control these diseases, and address ways to improve access to essential medicines and health technologies.
6. Getting the finances in order
This year has been described as one of the most challenging ever at the UN, which is being buffeted by extreme pressures on its finances. The US, a major donor announced that it would be leaving WHO in January, and other countries have also cut development and aid funding.
This year’s Assembly will see Member States negotiating a 50 per cent increase in the base budget, something that has been in the works since the 2022 meeting. If a funding boost is approved, it will provide a vital boost at a challenging time. WHO is also seeking additional voluntary contributions, and additional pledges are anticipated from member states and philanthropic organisations.
Follow the sessions at the World Health Assembly here.






![[Left to right] Ambassador Mxolisi Nkosi of South Africa; President of the 78th World Health Assembly Teodoro Herbosa; Dr. Majed Zemni of Tunisia, recipient of the 2025 Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion; and WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhano… [Left to right] Ambassador Mxolisi Nkosi of South Africa; President of the 78th World Health Assembly Teodoro Herbosa; Dr. Majed Zemni of Tunisia, recipient of the 2025 Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion; and WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhano…](https://global.unitednations.entermediadb.net/assets/mediadb/services/module/asset/downloads/preset/Libraries/Production%20Library/23-05-2025-WHO-Mandela-Award.jpg/image1170x530cropped.jpg)
